Eczema
What is eczema?
Atopic eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis is a very common chronic skin disease. It is very common in babies and small children. As many as 15-20% of children under the age of seven have eczema, which is a significant increase in the last 30 years. In 50% of cases, atopic eczema is gone by the age of six, but it can persist into adulthood.
What does eczema look like?
Eczema is a skin condition that manifests as inflammation, dryness, itching, or redness on the skin’s surface. The skin with atopic eczema is accompanied by itching, is very dry, and prone to irritation. The disease usually has two phases, an active or “acute” phase and an inactive phase. People prone to atopic eczema must protect their skin during the inactive phase so that the periods between active phases are as long and painless as possible. ↳
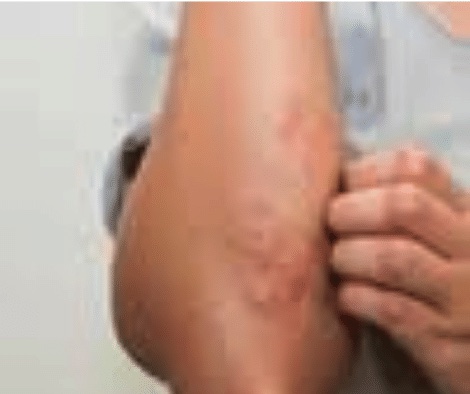
Scratching the area affected by eczema increases the possibility that various viruses, bacteria, and impurities will penetrate the skin and further worsen the itching. That discomfort accompanied by itching is quite frustrating for sufferers because even though scratching worsens the symptoms of eczema, it is very difficult to resist that urge.
Eczema affects people of all ages. It can cause irritation and pain caused by the formation of blisters and unpleasant cracks on the skin. In addition, many people suffer because of their appearance and do not feel comfortable in society.
The causes of eczema are not completely known, but some of them are listed below. Those are:
- genetics – 50%-70% of eczema sufferers have a parent who also has this disease
- perfumes or some deodorants
- friction in contact with some synthetic fibers or wool
- allergens such as dust mites, dust, pollen, animal hair, or mold
- stress
- heavy sweating
- various soaps
- fabric softeners
- central heating
- air conditioning devices
- diabetes can also be a cause of eczema
Eczema on the face
Eczema on the face is accompanied by very dry, tight, and itchy skin. It most often appears in newborns and small children. It most often occurs on the face, especially on the cheeks and chin. Over time, eczematous areas first appear on the neck, and skin folds around the elbows and wrists, and behind the knees.
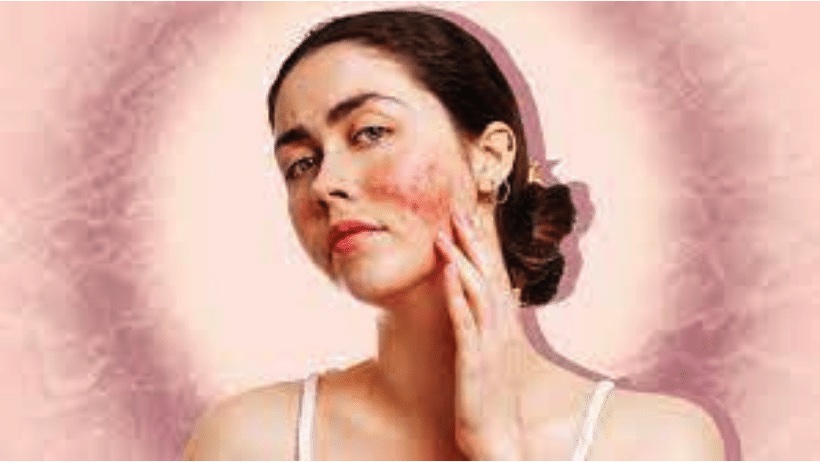
Symptoms of atopic eczema on the face are flaking, and rough and red spots. It include areas of very itchy dry skin, often with visible scratch marks. Symptoms of atopic eczema on a child’s face greatly affect a child’s self-esteem and can cause shame and anxiety. The good thing is that with appropriate treatment and regular care, atopic eczema can be effectively controlled and resolved. Sometimes even to the point where it stops being a problem.
As we have already emphasized, one of the main symptoms of eczema is dry skin. When the skin is very dry, its protection is not strong enough, the skin loses moisture faster and is more prone to inflammation and infections. That is why good hydration of the skin is the most important thing in the fight against eczema.
Eczema on the skin
Eczema-prone skin lacks natural moisture-retaining factors such as amino acids. In the same way, atopic skin deals with disorders in the creation of a protective layer of lipids. The skin’s protective layer weakens, and the lower layers are more susceptible to infection due to frequent scratching. ↳
Symptoms of atopic dermatitis are often its triggers. Moreover, if the skin is dry and itchy, the affected person will often scratch. Scratching reduces the protective function of the skin. As a result, the lower layers of the skin become more exposed and more sensitive to various infections and factors from the environment. When the bacteria get into the skin, they irritate, so the itching continues. In this way, a vicious circle is created in people prone to atopic skin.
The real cure for atopic eczema has still not been found and dermatologists have yet to discover it. But regardless, it has been proven that in some people, a certain number of factors affect the increased risk of the disease.
Those are:
- Genetics. There is a possibility that a child will develop atopic eczema if one or both parents suffer from health problems such as asthma or hay fever. The risk of disease increases proportionally so that if both parents have all three health problems, the possibility that the child will inherit the disease is also higher.
- Climate. In areas with a colder climate, there is a greater risk of atopic dermatitis. Likewise, living in polluted cities increases the risk of disease.
- Sex. Women are more prone to atopic eczema than men.
- Mother’s age. Children born in their mothers’ late reproductive period are more susceptible to the risk of atopic eczema than those born in their mothers’ younger period of life.
As the triggers for developing atopic eczema vary from person to person, with just a few lifestyle changes it is possible to significantly ease the symptoms of atopic eczema.
We will only mention some of them.
- Wearing soft cotton clothing in contact with the skin. Cotton is very pleasant to the skin and can be worn in layers even in winter. Materials that scratch a lot, such as wool, as well as fabrics that do not allow the skin to breathe, such as nylon, should be avoided as much as possible.
- Try avoiding heavy sweating as much as possible, maintaining low temperature and low humidity.
- Keeping a food diary can also help track triggers that affect atopic eczema. In the diary, you can record all the triggers that lead to the acute phase.
- Planning an annual holiday in climes with colder to moderate climates. Areas that are neither too hot nor too cold have a beneficial effect on skin prone to atopic eczema.
- Skin care products should be stored in a cool place, preferably in the refrigerator. Applying cooled skin preparations is very helpful in alleviating itching.
- Always wash new clothes before wearing them. New clothes may contain irritating dyes and odors in the fabric.
- If you are prone to scratching, wearing cotton gloves at night to prevent scratching while you sleep may help.
- Showering with warm or lukewarm water. The water should not be hot.
- Bathing should not be too long. 5-10 minutes is enough.
- When bathing, it is good to use bath oils because they provide additional care.
- Rough sponges and massage brushes should be avoided.
- Light exercise such as yoga can also be good for stress relief.
Eczema on hands
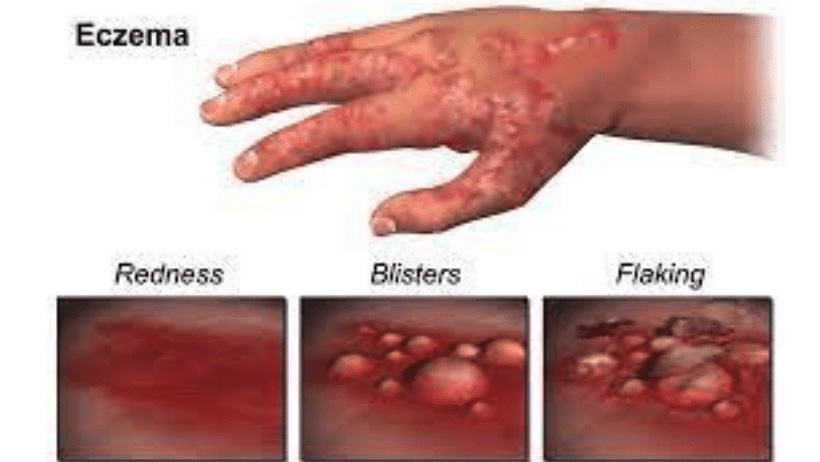
Eczema on the hands can be caused by different factors. It can be due to contact with some allergens (some substance that causes an allergic reaction) such as strong chemicals, other external factors (eg irritants such as soaps and detergents), and predispositions. Eczema on the hands can significantly reduce the quality of life and also lead to various problems. There are many types of hand eczema. Depending on the type, there are various topical therapies such as creams, ointments, lotions, and systemic therapies.
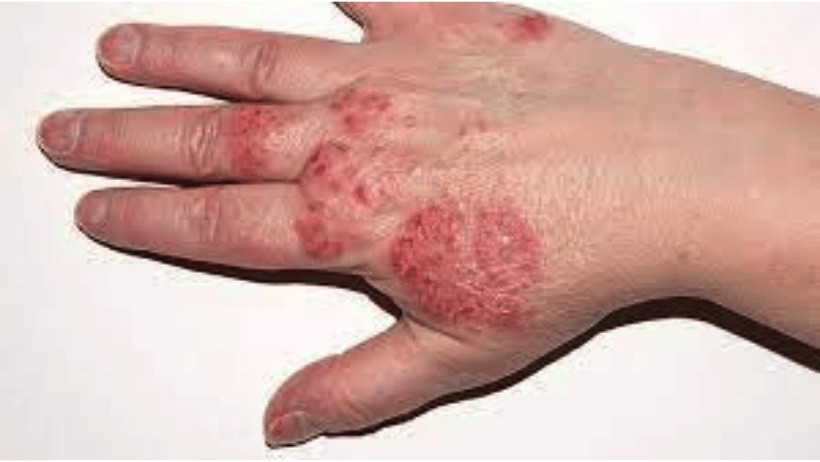
Eczema on the hands (also called dermatitis on the hands) is a very common phenomenon and unfortunately, affects one in twenty people. Symptoms can vary. Variations can range from mild dryness, redness and itching, to severely flaky and itchy hands. In very severe cases, painful cracks may appear on the skin that oozes or bleeds. With eczema on the hands, any part of the hand can be affected and the symptoms certainly differ from person to person.
Eczema on the hands
Eczema on the hands can appear in childhood, but more often it appears in adults. It very often affects people whose hands are in frequent contact with chemicals or other irritants during work. Eczema on the hands is not contagious, but it causes difficulties in everyday life and at the workplace.
Some people have a genetic predisposition to atopic eczema. They are certainly more sensitive to external irritants and allergens and are more likely to develop eczema on their hands.
However, people who do not have a genetic predisposition can also develop eczema on their hands. Due to its delicate structure, the skin on the hands is more prone to dryness than other parts of the body. Washing too often, cold weather, or chemicals in the workplace can damage the outer layers of the skin and lead to dryness, thus increasing the tendency to irritation. This condition is also called irritant contact dermatitis.
Eczema on legs
Eczema on the legs is an inflammatory process on the skin of the lower extremities. The disease is very often chronic and most often allergic in nature and caused by a combination of external and internal causes.
The most important thing is to determine the exact cause because causes can vary. For example, varicose veins (develops on the back of important varicose veins, and is accompanied by itching, burning, and redness of the skin), foot eczema (appears under the influence of external causes), and the like. The disease can occur as a result of long-term stress if the person had a viral infection, or due to various chronic diseases.
Causes of eczema
- Various allergenic substances on the skin
- Chemicals such as gasoline, various paints, household chemicals, cosmetic soap, etc.
- Sudden changes in temperature or climate changes
- Varicose veins
- Chronic viral disease
- Injury to some internal organs
- Weakening of the protective function of the body
- Wearing woolen clothes
- Fungal diseases
- Nervous breakdown or stressful situation
Treatment for eczema on the feet includes both local and general treatment methods. With local therapy, the degree of the disease is assessed. ↳
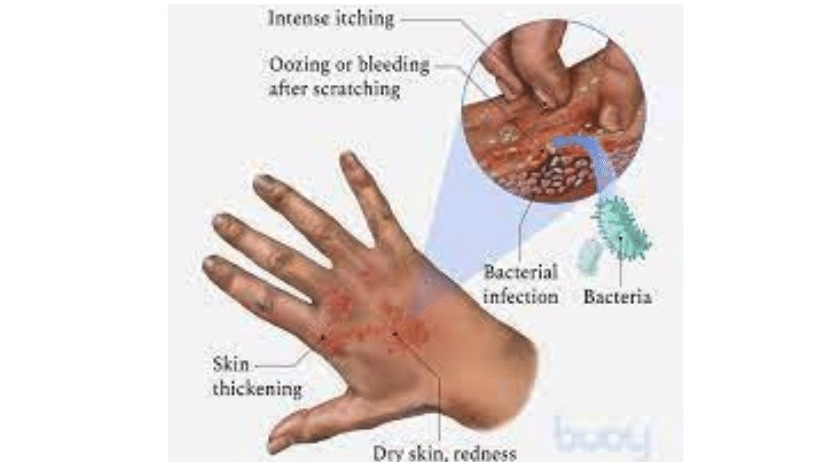
Regardless of the cause of foot eczema, it is recommendable for the patient to adhere to a special diet, which excludes products such as alcohol, smoked meat, hot spices, sweet and sour foods, chemical additives, and so on. It is vitally important to adhere to such a diet during the period of worsening of the disease.
Contact dermatitis
Speaking of contact dermatitis or contact eczema, we distinguish between non-allergic and allergic eczema, according to the clinical picture and the way it originates, with the fact that both forms can occur in an acute or chronic form.
Acute non-allergic contact dermatitis occurs as a result of a strong reaction after contact with an extremely strong external factor. The underlying cause is only an inflammatory process, without allergic or immunological events. The most common causes of eczema are chemicals based on acids and alkalis, various solvents, thinners, or strong exposure to X-ray, UV, or laser rays. Here, only the surface layer of the skin is damaged, and only at the point of contact. Changes are also sharply limited. The skin is red and slightly swollen, blisters may appear that are filled with clear or sometimes purulent contents. Peeling and cracking of the skin may occur. There is a feeling of burning and tightness with slight itching. Eczema can subside even without treatment.
Chronic non-allergic contact dermatitis occurs after long-term effects of chemical or strongly irritating substances on the skin. At the same time, they cause chronic damage to the skin because the lipid protective layer of the skin becomes thinner, the pH of the skin changes, and the normal bacterial flora is lost. Changes on the skin develop slowly, especially if one uses no protective equipment such as gloves or protective creams. The most common places that are exposed to these changes are the hands and fingers. The skin becomes very dry, and thickened, it can peel or develop very painful cracks.
Eczema cream
Eczema treatment can be very long-term and may require different therapy over a long period of time. There are various treatments that help relieve eczema such as:
- skin moisturizing creams or lotions
- creams or oral therapy to reduce itching or inflammation (eg corticosteroids)
- creams for restoring damaged skin
- antibiotics or other medicines that treat infection in open wounds or cracked skin
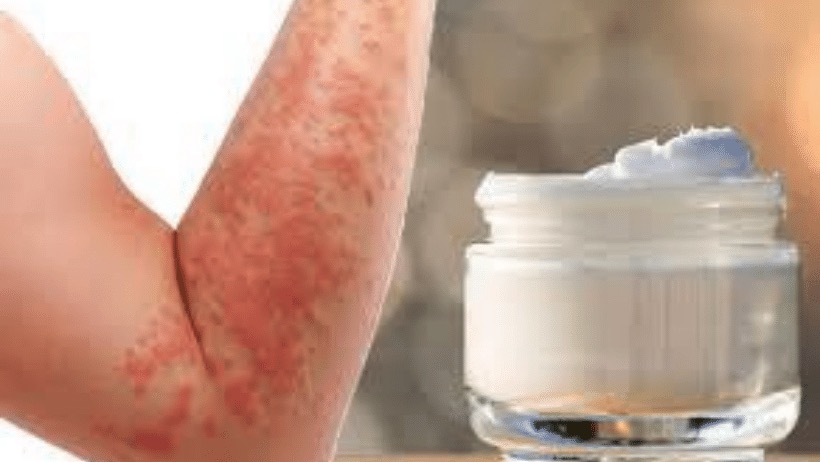
There are some simple steps you can take to reduce eczema symptoms:
- Treat the skin with moisturizing products, such as moisturizing creams or lotions. This is especially important after showering.
- Do not bathe in water hotter than 36°C and do not bathe for longer than 10-15 minutes.
- Use only mild soaps.
- Wear soft, breathable clothing. The best choice is cotton or linen. Synthetic fiber materials are not good for people prone to eczema.
- Regularly light up and ventilate the rooms where you stay.
